No edit summary |
No edit summary Tag: Visual edit |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| caption = The Battle of Stalingrad in 1942-43 |
| caption = The Battle of Stalingrad in 1942-43 |
||
| date = '''Start:''' September 1, 1939<br>'''End:''' September 2, 1945 |
| date = '''Start:''' September 1, 1939<br>'''End:''' September 2, 1945 |
||
| − | | place = North Africa, Europe, Pacific Ocean, Asia, Middle east |
+ | | place = [[North Africa]], [[Europe]], [[Pacific Ocean]], [[Asia]], [[Middle east]], [[Oceania]] |
| + | | result = Allied Victory : Collapse of Nazi Germany : Imperialistic Japan : Start of [[Cold War]] : Division of East/West Germany : Formation of United Nations |
||
| − | | result = Allied Victory |
||
| combatants_header = |
| combatants_header = |
||
| combatant1 = <center><big>'''Allies'''</big></center> |
| combatant1 = <center><big>'''Allies'''</big></center> |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<center>Soviet Union</center> |
<center>Soviet Union</center> |
||
<center>United States</center> |
<center>United States</center> |
||
| − | <center> |
+ | <center>United Kingdom</center> |
| + | <center>Poland</center> |
||
<center>France</center> |
<center>France</center> |
||
<center>China</center> |
<center>China</center> |
||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
| campaignbox = |
| campaignbox = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| + | '''World War II''' (''abr.'' '''WWII''' or '''WW2'''), also known as the '''Second World War''', was a [[World war|global war]] that lasted from 1939 to 1945, although related conflicts began earlier. It involved [[World War II by country|the vast majority of the world's countries]]—including all of the [[great power]]s—eventually forming two opposing [[military alliance]]s: the [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] and the [[Axis powers|Axis]]. It was the most widespread war in history and directly involved more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. In a state of [[total war]], the major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the [[war effort]], erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. World War II was the [[List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll|deadliest conflict]] in [[History of the world|human history]], marked by 50 million to 85 million fatalities, most of which were civilians in the Soviet Union and China. It included [[massacres]], the deliberate [[genocide]] of [[the Holocaust]], [[Strategic bombing during World War II|strategic bombing]], starvation, disease and the first use of [[nuclear weapon]]s in history.{{sfn|Gilbert|2001|p=291}}<ref>{{cite book |title=War, Violence, and Population: Making the Body Count |author=James A. Tyner |page=49 |date=3 March 2009 |publisher=The Guilford Press; 1 edition |isbn=1-6062-3038-7}}</ref>{{sfn|Sommerville|2008|loc=p. 5 (2011 ed.)}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/tyne/content/articles/2005/01/20/holocaust_memorial_other_victims_feature.shtml|title=BBC - Tyne - Roots - Non-Jewish Holocaust Victims : The 5,000,000 others|website=www.bbc.co.uk|accessdate=27 August 2017}}</ref> |
||
| − | '''World War II''' is to have officially begun on September 1, 1939 with the invasion of [[Poland]] by the [[German]] military in most Anglo-American and European accounts. However, a less Eurocentric understanding of world history would identify the start of the Second Sino-Japanese War on July 7, 1937 or the start of the Italo-Ethiopian War in 1935 as beginning points for the protracted global conflict. The Second World War was a result of various factors, including the flawed peace settlement following the [[World War I|First World War]] and geo-political grievances of the three main revisionist powers: Germany, [[Italy]], and [[Japan]]. |
||
| + | ==Political climate== |
||
| − | The rival international military alliances in the war were the United Nations, conventionally called the "[[Allies]]", and the [[Axis]] powers. [[France]] and Britain were the principal Allied powers in 1939, with the [[Soviet Union]] joining in 1941 following the German invasion and the [[United States]] joining in late 1941 following the Japanese attack on [[Pearl Harbor]] and the Philippines. [[Canada]], [[India]] and [[Australia]] also contributed immensely to the Allied war effort. Germany, Italy, and Japan were the principal Axis powers. [[Finland]], [[Hungary|Hungary and]] Romania also contributed much to the Axis war effort. Although technically neutral, both [[Spain]]and Sweden contributed "Blue Divisions" of fascist volunteers to the Eastern Front. Sweden also allowed German troops to use its railways to occupy [[Norway]]. Although a fascist dictatorship, [[Portugal]] continued to aid Britain Both alliances presented odd bedfellows memberships; liberal democratic Finland was a member of the Axis and authoritarian [[Cuba]] was a member of the Allies. |
||
| + | ===National Socialism in Germany=== |
||
| + | The Nazi Party and [[Adolf Hitler]] began to undergo power in 1919, and it started off with him joining the German Workers' Party. It was then renamed to the National Socialist German Workers' Party, or more commonly known as Nazi Party. In the 1920s, the Nazis had already latched onto the very weak political government of [[Weimar Republic|Germany]], making them able to express their ideals easier. As the years went on, Hitler rallied more and more people to join on his side, as he would "lead them to a better life". Germany after WWI was devastated by debt, which was worse than the United States.This made it even easier for Hitler to gain power. By the early 1930s, the Nazis had become the largest party in Germany. |
||
| + | By the 1929 market crash in the US, the communists and Nazis were able to denounce democracy, and have a chance to prove that their political ideology was better than the US'. This led to the democracy campaigners to suffer from heavy losses in the political elections due to a spread of word of how evil democracy is. At this time, the Nazis had about a million people who were apart of them. The Nazis had tried several times to put Hitler onto the Chancellor's seat but fell just short of it by other political leaders. However, the inability to gain control wasn't very short, as in 1933, he was appointed Chancellor of Germany. Many of the people who opposed the Nazis had failed to act against it, and Hitler was able to seize total control. |
||
| − | At the beginning of the war, Germany quickly seized the capital of Poland: Warsaw. Poland was home to the largest population of Jews in the world at the time, at more than three million. They found themselves under [[Nazism|Nazi]] rule. The Soviet Union invaded Eastern Poland, in part with the agreements in the Soviet Nazi non-aggression pact. France and Britain expected a [[File:300px-Infobox collage for WWII.png|thumb|218px|The bloody memories of World War II]]reenactment of World War I tactics, so they dug trenches. The Allied commanders also expected the Germans would attack France after the invasion of Poland. However, this was wrong, as Nazi Germany invaded [[Denmark]] and Norway in April, 1940, to secure iron ore being shipped from Sweden to Germany. Denmark surrendered immediately, while Norway was conquered in two months. As Allied leaders pondered where the next attack would take place, Nazi Germany moved it's tanks through the very lightly defended territory of the Ardenne. The panzers then swiftly cut through France with its infantry following behind. The British, trapped, evacuated their forces at Dunkirk. On June 22, an armistice was signed between France and Germany. The Netherlands and Belgium were also overrun. With France neutralized, Germany began an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Air_superiority <u>air superiority</u>] campaign over Britain (the [[Battle of Britain|<u>Battle of Britain</u>]]) to prepare for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operation_Sealion <u>an invasion</u>]. However, the air campaign failed, and the invasion of Britain was postponed indefinitely. Throughout this period, the neutral United States took measures to assist China and the Western Allies. In November 1939, the American [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neutrality_Acts_of_1930s <u>Neutrality Act</u>] was amended to allow [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cash_and_carry_(World_War_II) <u>"cash and carry"</u>] purchases by the Allies. 1941 was a major year for World War 2, as it witnessed the invasion of the Soviet Union and the attack on Pearl Harbor, which in turn, brought the United States into the war. Soviet counteroffensives were attempted at the German advance. However, most of them failed, and Kiev fell to the Germans. Japan knew the Allied powers were weakened, so Japan attacked French Indochina. Great Britain and the United States responded by freezing Japanese assets, and the U.S. put a complete oil embargo on Japan. Japan had a choice between abandoning their empire, or taking the resources they needed by force. Japan decided to take the resources. Japan then invaded the Dutch East indies, Thailand, Hong Kong, the Philippines, and attacked the American naval fleet at Pearl Harbor. The United States declared war on Japan on December 8th, the day after the attack on Pearl Harbor. In 1942, the Axis advance stopped, with the Germans being pushed out of North Africa. The battle of Stalingrad was a severe defeat for the German army. The Japanese navy had been eliminated as an effictive fighting force at the battle of Midway. The Allies attacked the Vichy holdings in North Africa as well. In 1943, Soviet offensives had eliminated any hopes for a German victory. A disastrous attack on the Kursk bulge exhausted German forces. On July 9, 1943, the Allied forces from North Africa, along with many reinforcements, invaded Sicily. The invasion of Sicily paved the way for an invasion of the Italian mainland. In September, Italy signed an armistice with the Allies, and Allied forces invaded mainland Italy. However, the Germans then established a puppet state, called the Italian Social Republic. The Japanese were pushed out of New Guinea as well during 1943. In 1944, American, Britain, and Canadian forces had launched Operation Overlord, the liberation of France from Nazi rule. Local uprisings in France also assisted the Allies. But an attempted liberation of the Netherlands failed. The Soviets launched a massive operation as well, resulting in the almost complete destruction of Geman forces in Belarus. Encouraged by the Soviet advance, Polish uprisings exploded, and two-thirds of Warsaw were taken by resistance forces. But the resistance had no response to Nazi armor and airpower, and the revolt was put down. By then, Soviet forces pushed into Nazi occupied Yugoslavia. The United States by then had also began to liberate the Philippines. Germany launched a massive counter offensive in the ardenne which would continue into 1945. In 1945, the Ardenne counter-offensive had been repulsed, and the Allies had finally entered Germany. On April 30th, in the face of defeat, and with the Red Army advancing into Berlin, Hitler committed suicide. In May 1945, the Third Reich collapsed. The Philippines had been finally secured in 1945, and Okinawa had been seized. The United dropped two atomic bombs on Japan, as well as the Soviet Union invading Japanese occupied Manchuria. Japanese leaders realized that the United States had a new deadly weapon, and also knew the Soviet Union was willing to bear the heavy losses if they invaded Japan. The Japanese empire surrendered, and World War 2 ended. World War Two had some of the worst atrocities ever committed in recorded history. The Holocaust had killed six million Jews, as well as four million others. |
||
| + | Eventually the Nazis began to suspend civil rights and political opposition. All of the communists were kicked out of any seat in power. He continue sto take away freedoms from the people. He even got a stamped letter saying that he had the free will to do what he wants without consent of parliament. He and his party also spread antisemitism amongst the people, allowing them to have a common enemy. Hitler took his control and used it with force and intimidation. |
||
| − | It was the greatest confrontation ever. It saw the rise and fall of some totalitarisms: [[Nazism]] in Germany and [[Fascism]] in Italia. World War II would bring an entirely different war: the Cold War. |
||
| + | ===Fascism in Italy=== |
||
| + | At the same time in [[Italy]], [[Benito Mussolini]] was gaining power from a new political ideology called fascism. They would claim themselves to be the best nationalists and wanted what was only right for their country. The Italian fascists took against Liberalism and gathered a stronger suit of being a heavily conservative ideology. The people known as the Blackshirts, which were a mix of World War I veterans and ideal socialists, were taken under Mussolini's wing. However, it wasn't just democracy that was against fascism, but instead feminists as well, as Mussolini had a deal of women's suffrage movement in Italy, which was partially taken into account by the fascists. |
||
| + | ===Beginnings=== |
||
| − | ==Origins of World War II== |
||
| + | World War II officially began on September 1, 1939 with the German invasion of Poland, which was to look like a Polish espionage mission against Germany. At this time, Hitler made a non-aggression pact with [[Joseph Stalin]] of the Soviet Union, which that they wouldn't attack each other. They also made an agreement to invade Poland together: Germany from the west, and the Soviets from the east. Two days later, the UK and France, along with the British Commonwealth, declared war on Germany. The Germans made a new style of warfare, Blitzkrieg, which was a lightning-fast attack with full armor. Poland fell in just a week and a half. The remaining soldiers of Poland evacuated to Romania. |
||
| − | World War Two started in 1939 when Germany and the Soviet Union invaded Poland. |
||
| + | |||
| + | On the sixth of October of that year, Hitler wanted a peace agreement with France and the UK. Chamberlain, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom at that time, rejected the peace offering. Hitler answered to the denial with a full attack against France. Due to bad weather, it was postponed to Spring of the next year. Meanwhile in the Soviet Union, they were stationing troops along twith he Baltic nations, as for peace. Finland rejected this idea, causing the Soviets to invade Finland. This gave the USSR bad relations with the Allies, causing the Russian seat to be kicked out of the League of Nations. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==Blitzkrieg== |
||
| + | [[File:Maginot_Line.png|thumb|320px]] |
||
| + | Spring of 1940 Germany invaded [[Denmark]] and [[Norway]], both falling in just two months. By this time, the UK was doing nothing to protect themselves, which forced Chamberlain out of office, whom was replaced by [[Winston Churchill]]. Before invading France, Germany invaded [[Belgium]], the [[Netherlands]], and [[Luxembourg]] for a closer front. The French were using an outdated form of military equipment, which wouldn't hold against the German's Blitzkrieg offensive. However, the French also put their strongest fortifications on the [[Maginot Line]] (French fortifications built in the 1930s to protect themselves from the growing German threat), which the Germans easily avoided by going around the Line by going through Belgium. France did not expect thi, and quickly abandoned their posts, leaving all of the artillery behind. As the French were fleeing for their lives, Italy declared war on both the UK and Franc, and invaded them from the south. Paris fell to the Germans soon after and France surrendered. The remaining French militants were being evacuated off the coast into the UK. France was then divided into Italian zones and German zones. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ariel strategy== |
||
| + | By now Hitler had his sights on the UK. He figured if he could get the United Kingdom, he could move across north and invade Canada, and finally the United States. In order to do this, he ordered for bombers and fighter planes to attack the city of London in hopes of gaining air superiority. Then he could move on to destroying the ships blocking the English Channel, and finally, move-in ships carrying soldiers to invade Britain. The Germans began bombing, in hopes of succeeding, as they have so far never lost in the war. Over the course of several months, the Royal Air Force (RAF) managed to keep the Germans from attaining air superiority, and eventually Hitler called back his bombers. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==Submarine strategy== |
||
| + | The Germans had been using U-boats for the first and now the second World War. They're easy and cheap to make, which is why Germans continued to build them. Hitler figured that they should build a battleship, which would go around and destroy all of the other battleships that the Allies had. After construction, Hitler was proud of creating the ''Bismarck'', which lived a short time before being destroyed by small British boats. Hitler wanted to make another, but was advised to stay with the U-boats, as building another battleship would be too expensive and not worth it. |
||
== Belligerents == |
== Belligerents == |
||
| + | {| |
||
| − | <span style="font-size:17px;">Allies</span> |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | <span style="font-size:17px;">Allied Powers</span> |
||
*[[United Kingdom]] |
*[[United Kingdom]] |
||
*[[Soviet Union]] |
*[[Soviet Union]] |
||
| Line 70: | Line 89: | ||
*[[Cuba]] |
*[[Cuba]] |
||
*[[Mexico]] |
*[[Mexico]] |
||
| − | + | ;Client States/ Colonies |
|
*[[India]] |
*[[India]] |
||
*[[Philippines]] |
*[[Philippines]] |
||
*[[Mongolia]] |
*[[Mongolia]] |
||
| + | ;Leaders |
||
| − | === Axis === |
||
| + | *[[Winston Churchill]]: United Kingdom |
||
| + | *[[Franklin D. Roosevelt|Franklin Roosevelt]]: United States |
||
| + | *[[Joseph Stalin]]: Soviet Union |
||
| + | *[[Chiang Kai-shek]]: China |
||
| + | *[[Władysław Sikorski]]: Poland |
||
| + | *[[Charles de Gaulle]]: Free France |
||
| + | *[[Peter Fraser]]: New Zealand |
||
| + | *[[William Lyon Mackenzie King]]: Canada |
||
| + | *[[Getulio Vargas]] : Brazil |
||
| + | *[[Jan Smuts]]: South Africa |
||
| + | *[[John Curtin]]: Australia |
||
| + | *[[Manuel Ávila Camacho]]: Mexico |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | <span style="font-size:17px;">Axis Powers</span> |
||
*[[Germany]] |
*[[Germany]] |
||
*[[Japan]] |
*[[Japan]] |
||
| Line 81: | Line 114: | ||
*[[Romania]] |
*[[Romania]] |
||
*[[Bulgaria]] |
*[[Bulgaria]] |
||
| + | ;Co-Belgerents |
||
| − | ====Co-Belgets==== |
||
*[[Finland]] |
*[[Finland]] |
||
*[[Thailand]] |
*[[Thailand]] |
||
*[[Iraq]] |
*[[Iraq]] |
||
| − | + | ;European Client States |
|
*[[Croatia]] |
*[[Croatia]] |
||
*[[Slovakia]] |
*[[Slovakia]] |
||
*[[Albania]] |
*[[Albania]] |
||
| − | + | ;Japan's puppet states |
|
*[[Manchukuo]] |
*[[Manchukuo]] |
||
*[[China-Nanjing]] |
*[[China-Nanjing]] |
||
| Line 97: | Line 130: | ||
*[[Azad Hind]] |
*[[Azad Hind]] |
||
*[[Vietnam]] |
*[[Vietnam]] |
||
| + | ;Leaders |
||
| − | |||
| − | == Leaders == |
||
| − | |||
| − | ===Allies=== |
||
| − | *[[Winston Churchill]]: United Kingdom |
||
| − | *[[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]: United States |
||
| − | *[[Charles de Gaulle]]: Free France |
||
| − | *[[Joseph Stalin]]: Soviet Union |
||
| − | |||
| − | ===Axis=== |
||
*[[Adolf Hitler]]: Germany |
*[[Adolf Hitler]]: Germany |
||
*[[Benito Mussolini]]: Italy |
*[[Benito Mussolini]]: Italy |
||
*[[Hideki Tojo]]: Japan |
*[[Hideki Tojo]]: Japan |
||
| + | *[[Miklos Horthy]]: Hungary |
||
| + | *[[Ion Antonescu]]: Romania |
||
| + | *[[Boris III of Bulgaria|Boris III]] : Bulgaria |
||
| + | <br><br> |
||
| + | |} |
||
==Major Battles== |
==Major Battles== |
||
| + | {| class="wikitable collapsible" width="100%" |
||
| + | !colspan="7"|<big>Major Battles</big> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>'''Battle'''</center> || <center>'''Countries'''</center> || <center>'''Date'''</center> || <center>'''Victory'''</center> || <center>'''Type of Battle'''</center> || <center>'''Casualties'''</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |colspan="7" align=center|'''Blitzkrieg''' |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Invasion of Poland]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Poland<br />Germany<br />Soviet Union</center> |
||
| + | |<center>September 1, 1939 - October 6, 1939</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Axis</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>256,800</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of France]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>France<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>May 10, 1940 - June 22, 1940</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Axis</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>523,650</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Britain]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Britain<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>July 10, 1940 - October 31, 1940</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Arial</center> |
||
| + | |<center>93,880</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |colspan="7" align=center|'''The War in the Mediterranean''' |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of El Alamein]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Britain<br />Germany<br />Italy</center> |
||
| + | |<center>October 23, 1942 - November 11, 1942</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>44,102</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Anzio]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Britain<br />United States<br />Germany<br />Italy</center> |
||
| + | |<center>January 22, 1944 - June 5, 1944</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>12,000</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Monte Cassino]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Britain<br />United States<br />France<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>January 17, 1944 - May 18, 1944</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>75,000</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |colspan="7" align=center|'''The Invasion of the Soviet Union''' |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[The Battle of Leningrad|Siege of Leningrad]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Soviet Union<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>September 8, 1941 - January 27, 1944</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Siege</center> |
||
| + | |<center>5,058,051</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Moscow]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Soviet Union<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>October 2, 1941 - January 7, 1942</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>528,000</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Stalingrad]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Soviet Union<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>August 23, 1942 – February 2, 1943</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Siege</center> |
||
| + | |<center>1,979,619</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Kursk]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Soviet Union<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>July 5, 1943 – July 16, 1943</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>684,499</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |colspan="7" align=center|'''Germany's Defeat''' |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Normady Landings]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>United States<br />Britain<br />Canada<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>June 6, 1944</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Naval Invasion</center> |
||
| + | |<center>19,000</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Berlin]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Soviet Union<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>April 16, 1945 – May 2, 1945</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>181,116</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of Arnhem]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Britain<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>September 17, 1944 - September 26, 1944</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Axis</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>3,284</center> |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |<center>[[Battle of the Bulge]]</center> |
||
| + | |<center>United States<br />Britain<br />Germany</center> |
||
| + | |<center>December 16, 1944 – January 25, 1945</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Allied</center> |
||
| + | |<center>Land</center> |
||
| + | |<center>158,108</center> |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | ==War in The Pacific== |
||
| − | <u>Blitzkrieg</u> - the "lightning fast" Axis conquests of many countries such as Poland, Austria, France, etc. |
||
| − | *[[Defeat of Poland]], occurred in 1939, land battle, German victory |
||
| − | *[[Battle of France]], occurred in 1940, land battle, German victory |
||
| − | *[[Battle of Britain]], occurred in 1940, aerial battle, British victory |
||
| − | <u>The War in the Mediterranean</u> |
||
| − | *[[The battle of El Alamein]], occurred in 1942, land battle, Allied victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Anzio]], occurred in 1944, land battle, Allied victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Monte Cassino]], occurred in 1944, land battle, Allied victory |
||
| − | <u>Invasion of Russia</u> |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Leningrad]], occurred in 1941-1944, siege, Allied (Soviet) Victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Moscow]], occurred in 1941-1942, land battle, Allied (Soviet) Victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Stalingrad]], occurred in 1942-1943, siege, Allied (Soviet) Victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Kursk]], occurred in 1943, land battle, Allied (Soviet) Victory |
||
| − | <u>Germany's defeat</u> |
||
| − | *The Normandy Landings of [[D-Day]], occurred in 1944, land/naval battle, Allied Victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Arnhem]], occurred in 1944, land battle, German Victory |
||
| − | *[[The battle of Berlin]], occurred in 1945, land battle, Soviet Victory |
||
| − | <u>The War in The Pacific</u> |
||
*[[The Battle of the Philippines]], occurred in 1941-1942, land battle, Japanese Victory |
*[[The Battle of the Philippines]], occurred in 1941-1942, land battle, Japanese Victory |
||
*[[The Battle of Singapore]], occurred in 1942, siege, Japanese Victory |
*[[The Battle of Singapore]], occurred in 1942, siege, Japanese Victory |
||
| Line 141: | Line 264: | ||
*[[The Battle of Okinawa]], occurred in 1945, land battle, Allied (American) Victory |
*[[The Battle of Okinawa]], occurred in 1945, land battle, Allied (American) Victory |
||
| + | == Timeline == |
||
| − | {{History of America}} |
||
| + | {| class="article-table" |
||
| + | !Date |
||
| + | ! |
||
| + | '''Battle''' |
||
| + | !Detailed Information |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |January 1933 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Adolf Hitler]] becomes [[Germany]]'s Chancellor. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |July 1937 |
||
| + | |[[Second Sino - Japanese War]] |
||
| + | |The [[Japan|Japan Empire]] invades the [[ China|Republic of China]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |March - Oct 1938 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Germany]] annexes [[Austria]] and the [[Sudetenland]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |March 1939 |
||
| + | |[[Germany invades Czechoslovakia]] |
||
| + | |[[Germany]] had occupied [[Czechoslovakia]] despite the assurances given by him. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |March /April 1939 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Britain|The Great Britain]] rearms and reassures [[Poland]], who was being threatened by the [[Fuhrer]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |23 August 1939 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Hitler]] and [[Stalin]] signed a non - aggression pact which included secret clauses for the division of [[Poland]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |1 September 1939 |
||
| + | |[[Germany invades Poland]] |
||
| + | |[[Germany]] had occupied [[Poland]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |3 September 1939 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Britain]] and [[France]] declare war on [[Germany]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |17 September 1939 |
||
| + | |[[The Soviet Union invades Poland]] |
||
| + | |[[Soviet Union|The Soviet Union]] invades [[Poland]], honoring the German - Soviet pact. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |September 1939 - May 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Phoney War]] |
||
| + | |The months following [[Britain]]’s declaration of war are referred to as the ‘Phoney War’ because [[Britain]] saw no military action. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |November 1939 - March 1940 |
||
| + | |[[The Winter War]] |
||
| + | |[[Soviet Union|The Soviet Union]] occupied [[Finland]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |April 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Germany invades Luxembourg, Denmark and Norway]] |
||
| + | |[[Germany]] occupied [[Luxembourg]], [[Denmark]] and Norway. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |10 May 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Blitzkrieg]] |
||
| + | |[[Hitler]] launched his [[blitzkrieg]] ( Lightning War ) against [[Netherlands]] and [[Belgium]]. Both countries were occupied. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |13 May 1940 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Neville Chamberlain]] resigned after pressure from Labour members for a more active prosecution of the war and [[Winston Churchill]] became the new head of the wartime coalition government. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |26 May 1940 - 4 June 1940 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |The [[British]] commander-in-chief, [[General Gort]], had been forced to retreat to the coast at [[Dunkirk]]. The troops waited, under merciless fire, to be taken off the beaches. A call went out to all owners of sea-worthy vessels to travel to Dunkirk to take the troops off the beaches of Dunkirk. More than 338,000 men were rescued, among them some 140,000 French who would form the nucleus of the [[Free French army]] under a little known general, [[Charles de Gaulle]]. More than 330,000 surrounded [[Allies|Allied]] soldiers escape into England. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |May 1940 - June 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Battle of France]] |
||
| + | |[[Germany]]'s Mobile Warfare defeats the [[Allies]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |10 June 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Italy invades France]] |
||
| + | |[[Italy]] occupied [[France]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |11 June 1940 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Italy]] enter war on side of [[Axis]] powers |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |22 June 1940 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |France signs armistice with Germany |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |10 July 1940 – 31 October 1940 |
||
| + | |[[Battle of Britain]] |
||
| + | |The Battle of Britain comprised four phases:<br /> |
||
| + | 1. During July, Hitler sent his Luftwaffe bombers to attack British ports. His aim was also to assess the speed and quality of response by the RAF.<br /> |
||
| + | 2. During August, the attacks on shipping continued but bombing raids were concentrated on RAF airfields.<br /> |
||
| + | 3. The Blitz – From September 7th, the city of London was heavily bombed. Hitler hoped to destroy the morale of the British people.<br /> |
||
| + | 4. Night Bombing – With the failure of daylight bombing raids, Hitler began a series of nightly bombing raids on London and other important industrial cities. |
||
| + | [[Royal Air Force|The Royal Air Force]] faced the [[Laftwaffe]]. The RAF defended the skies and by October 31, the raids had ceased. |
||
| − | [[pl:II wojna światowa]] |
||
| + | |- |
||
| − | [[Category:Japan]] |
||
| + | |9 September 1940 |
||
| − | [[Category:Great Britain]] |
||
| + | |[[Italy invades British' Egypt]] |
||
| − | [[Category:Germany]] |
||
| + | |[[Italy]] occupies [[British]]' [[Egypt]], the [[North African Campaign]] begins. |
||
| − | [[Category:The Netherlands]] |
||
| + | |- |
||
| − | [[Category:France]] |
||
| + | |22 Sept 1940 |
||
| − | [[Category:Austria]] |
||
| + | |[[Japan invades French Indochina]] |
||
| − | [[Category:China]] |
||
| + | |[[Japan]] occupies [[French Indochina]], effectively blockading [[China]] from importing arms. |
||
| − | [[Category:Wars]] |
||
| + | |- |
||
| − | [[Category:Major Battles]] |
||
| + | |25 September 1940 |
||
| − | [[Category:World War]] |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |Tripartite Pact of mutual alliance was signed by [[Germany]], [[Italy]] and [[Japan]]. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |November 1940 - March 1941 |
||
| + | |<nowiki>-</nowiki> |
||
| + | |[[Hungary]], [[Romania]] and [[Bulgaria]] joined the [[Axis]] Powers. |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== |
||
| + | <references/>[[pl:II wojna światowa]] |
||
[[Category:World War II]] |
[[Category:World War II]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Wars]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Modern Age]] |
||
Revision as of 14:41, 15 November 2019
World War II (abr. WWII or WW2), also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945, although related conflicts began earlier. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history and directly involved more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. In a state of total war, the major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, marked by 50 million to 85 million fatalities, most of which were civilians in the Soviet Union and China. It included massacres, the deliberate genocide of the Holocaust, strategic bombing, starvation, disease and the first use of nuclear weapons in history.[1][2][3][4]
Political climate
National Socialism in Germany
The Nazi Party and Adolf Hitler began to undergo power in 1919, and it started off with him joining the German Workers' Party. It was then renamed to the National Socialist German Workers' Party, or more commonly known as Nazi Party. In the 1920s, the Nazis had already latched onto the very weak political government of Germany, making them able to express their ideals easier. As the years went on, Hitler rallied more and more people to join on his side, as he would "lead them to a better life". Germany after WWI was devastated by debt, which was worse than the United States.This made it even easier for Hitler to gain power. By the early 1930s, the Nazis had become the largest party in Germany.
By the 1929 market crash in the US, the communists and Nazis were able to denounce democracy, and have a chance to prove that their political ideology was better than the US'. This led to the democracy campaigners to suffer from heavy losses in the political elections due to a spread of word of how evil democracy is. At this time, the Nazis had about a million people who were apart of them. The Nazis had tried several times to put Hitler onto the Chancellor's seat but fell just short of it by other political leaders. However, the inability to gain control wasn't very short, as in 1933, he was appointed Chancellor of Germany. Many of the people who opposed the Nazis had failed to act against it, and Hitler was able to seize total control.
Eventually the Nazis began to suspend civil rights and political opposition. All of the communists were kicked out of any seat in power. He continue sto take away freedoms from the people. He even got a stamped letter saying that he had the free will to do what he wants without consent of parliament. He and his party also spread antisemitism amongst the people, allowing them to have a common enemy. Hitler took his control and used it with force and intimidation.
Fascism in Italy
At the same time in Italy, Benito Mussolini was gaining power from a new political ideology called fascism. They would claim themselves to be the best nationalists and wanted what was only right for their country. The Italian fascists took against Liberalism and gathered a stronger suit of being a heavily conservative ideology. The people known as the Blackshirts, which were a mix of World War I veterans and ideal socialists, were taken under Mussolini's wing. However, it wasn't just democracy that was against fascism, but instead feminists as well, as Mussolini had a deal of women's suffrage movement in Italy, which was partially taken into account by the fascists.
Beginnings
World War II officially began on September 1, 1939 with the German invasion of Poland, which was to look like a Polish espionage mission against Germany. At this time, Hitler made a non-aggression pact with Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, which that they wouldn't attack each other. They also made an agreement to invade Poland together: Germany from the west, and the Soviets from the east. Two days later, the UK and France, along with the British Commonwealth, declared war on Germany. The Germans made a new style of warfare, Blitzkrieg, which was a lightning-fast attack with full armor. Poland fell in just a week and a half. The remaining soldiers of Poland evacuated to Romania.
On the sixth of October of that year, Hitler wanted a peace agreement with France and the UK. Chamberlain, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom at that time, rejected the peace offering. Hitler answered to the denial with a full attack against France. Due to bad weather, it was postponed to Spring of the next year. Meanwhile in the Soviet Union, they were stationing troops along twith he Baltic nations, as for peace. Finland rejected this idea, causing the Soviets to invade Finland. This gave the USSR bad relations with the Allies, causing the Russian seat to be kicked out of the League of Nations.
Blitzkrieg
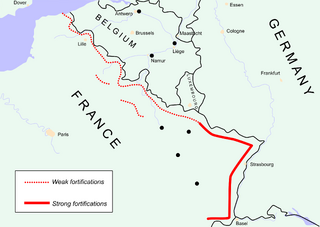
Spring of 1940 Germany invaded Denmark and Norway, both falling in just two months. By this time, the UK was doing nothing to protect themselves, which forced Chamberlain out of office, whom was replaced by Winston Churchill. Before invading France, Germany invaded Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg for a closer front. The French were using an outdated form of military equipment, which wouldn't hold against the German's Blitzkrieg offensive. However, the French also put their strongest fortifications on the Maginot Line (French fortifications built in the 1930s to protect themselves from the growing German threat), which the Germans easily avoided by going around the Line by going through Belgium. France did not expect thi, and quickly abandoned their posts, leaving all of the artillery behind. As the French were fleeing for their lives, Italy declared war on both the UK and Franc, and invaded them from the south. Paris fell to the Germans soon after and France surrendered. The remaining French militants were being evacuated off the coast into the UK. France was then divided into Italian zones and German zones.
Ariel strategy
By now Hitler had his sights on the UK. He figured if he could get the United Kingdom, he could move across north and invade Canada, and finally the United States. In order to do this, he ordered for bombers and fighter planes to attack the city of London in hopes of gaining air superiority. Then he could move on to destroying the ships blocking the English Channel, and finally, move-in ships carrying soldiers to invade Britain. The Germans began bombing, in hopes of succeeding, as they have so far never lost in the war. Over the course of several months, the Royal Air Force (RAF) managed to keep the Germans from attaining air superiority, and eventually Hitler called back his bombers.
Submarine strategy
The Germans had been using U-boats for the first and now the second World War. They're easy and cheap to make, which is why Germans continued to build them. Hitler figured that they should build a battleship, which would go around and destroy all of the other battleships that the Allies had. After construction, Hitler was proud of creating the Bismarck, which lived a short time before being destroyed by small British boats. Hitler wanted to make another, but was advised to stay with the U-boats, as building another battleship would be too expensive and not worth it.
Belligerents
|
Allied Powers
|
Axis Powers
|
Major Battles
| Major Battles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blitzkrieg | ||||||
Germany Soviet Union |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
| The War in the Mediterranean | ||||||
Germany Italy |
||||||
United States Germany Italy |
||||||
United States France Germany |
||||||
| The Invasion of the Soviet Union | ||||||
Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
| Germany's Defeat | ||||||
Britain Canada Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
Germany |
||||||
Britain Germany |
||||||
War in The Pacific
- The Battle of the Philippines, occurred in 1941-1942, land battle, Japanese Victory
- The Battle of Singapore, occurred in 1942, siege, Japanese Victory
- The Battle of Coral Sea, occurred in 1942, naval battle, American Victory
- The Battle of Guadalcanal, occurred in 1942-1943, land battle, Allied (American) Victory
- The Battle of Midway, occurred in 1942, naval battle, Allied (American) Victory
- The Battle of Leyte Gulf, occurred in 1944, land battle, Allied (American) Victory
- The Battle of Philippine Sea, occurred in 1944, Allied (American) Victory
- The Battle of Iwo Jima, occurred in 1945, land battle, Allied (American) Victory
- The Battle of Okinawa, occurred in 1945, land battle, Allied (American) Victory
Timeline
| Date |
Battle |
Detailed Information |
|---|---|---|
| January 1933 | - | Adolf Hitler becomes Germany's Chancellor. |
| July 1937 | Second Sino - Japanese War | The Japan Empire invades the Republic of China. |
| March - Oct 1938 | - | Germany annexes Austria and the Sudetenland. |
| March 1939 | Germany invades Czechoslovakia | Germany had occupied Czechoslovakia despite the assurances given by him. |
| March /April 1939 | - | The Great Britain rearms and reassures Poland, who was being threatened by the Fuhrer. |
| 23 August 1939 | - | Hitler and Stalin signed a non - aggression pact which included secret clauses for the division of Poland. |
| 1 September 1939 | Germany invades Poland | Germany had occupied Poland. |
| 3 September 1939 | - | Britain and France declare war on Germany. |
| 17 September 1939 | The Soviet Union invades Poland | The Soviet Union invades Poland, honoring the German - Soviet pact. |
| September 1939 - May 1940 | Phoney War | The months following Britain’s declaration of war are referred to as the ‘Phoney War’ because Britain saw no military action. |
| November 1939 - March 1940 | The Winter War | The Soviet Union occupied Finland. |
| April 1940 | Germany invades Luxembourg, Denmark and Norway | Germany occupied Luxembourg, Denmark and Norway. |
| 10 May 1940 | Blitzkrieg | Hitler launched his blitzkrieg ( Lightning War ) against Netherlands and Belgium. Both countries were occupied. |
| 13 May 1940 | - | Neville Chamberlain resigned after pressure from Labour members for a more active prosecution of the war and Winston Churchill became the new head of the wartime coalition government. |
| 26 May 1940 - 4 June 1940 | - | The British commander-in-chief, General Gort, had been forced to retreat to the coast at Dunkirk. The troops waited, under merciless fire, to be taken off the beaches. A call went out to all owners of sea-worthy vessels to travel to Dunkirk to take the troops off the beaches of Dunkirk. More than 338,000 men were rescued, among them some 140,000 French who would form the nucleus of the Free French army under a little known general, Charles de Gaulle. More than 330,000 surrounded Allied soldiers escape into England. |
| May 1940 - June 1940 | Battle of France | Germany's Mobile Warfare defeats the Allies. |
| 10 June 1940 | Italy invades France | Italy occupied France. |
| 11 June 1940 | - | Italy enter war on side of Axis powers |
| 22 June 1940 | - | France signs armistice with Germany |
| 10 July 1940 – 31 October 1940 | Battle of Britain | The Battle of Britain comprised four phases: 1. During July, Hitler sent his Luftwaffe bombers to attack British ports. His aim was also to assess the speed and quality of response by the RAF. The Royal Air Force faced the Laftwaffe. The RAF defended the skies and by October 31, the raids had ceased. |
| 9 September 1940 | Italy invades British' Egypt | Italy occupies British' Egypt, the North African Campaign begins. |
| 22 Sept 1940 | Japan invades French Indochina | Japan occupies French Indochina, effectively blockading China from importing arms. |
| 25 September 1940 | - | Tripartite Pact of mutual alliance was signed by Germany, Italy and Japan. |
| November 1940 - March 1941 | - | Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria joined the Axis Powers. |
References
- ↑ Gilbert 2001, p. 291.
- ↑ James A. Tyner (3 March 2009). War, Violence, and Population: Making the Body Count. The Guilford Press; 1 edition, 49. ISBN 1-6062-3038-7.
- ↑ Sommerville 2008, p. 5 (2011 ed.).
- ↑ BBC - Tyne - Roots - Non-Jewish Holocaust Victims : The 5,000,000 others. Retrieved on 27 August 2017.
